From pasta to chocolate and now 3D-printed meat, 3D-printed food is becoming increasingly popular. And while there is resistance against 3D-printed meat, the practice is here to stay.
With an increasing number of people adopting vegan, flexitarian, or vegetarian eating practices, coupled with the rising issues with livestock, alternative options that taste like meat are gaining in popularity.
In this guide, we’ll answer questions like what is 3D meat and explore the concept in greater depth.

What Is 3D Meat?
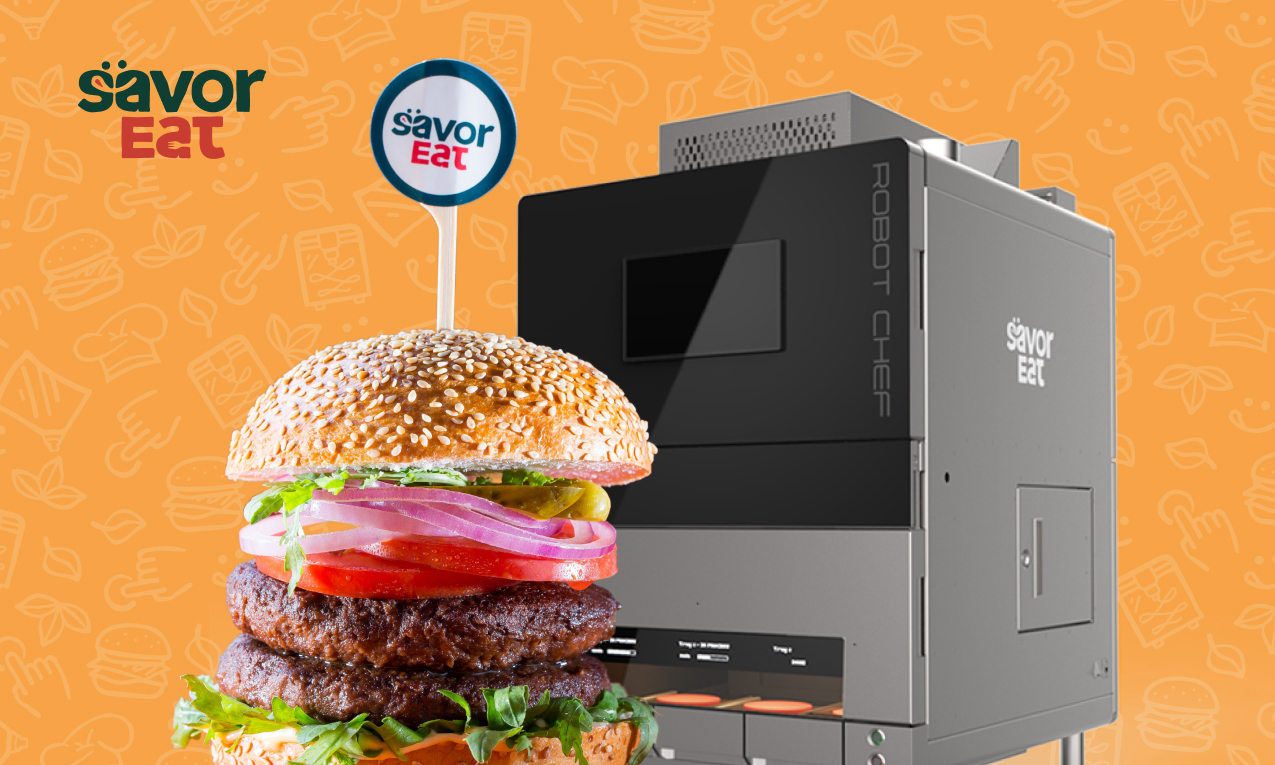
3D meat or 3D printed meat is a type of cultured or created meat made using 3D printers and additive manufacturing techniques, along with artificial intelligence and material science.
One approach involves feeding the printer cultured animal cells that are ‘printed’ into meat-like forms. Think of a regular printer, but instead of ink, you feed it a viscous consumable material, and you can eat the final product.
Note that 3D printed meat is only the process of producing the meat—it must still be cooked before it can be consumed. The 3D printing process only involves printing or projecting the material onto a surface in the desired shape.
Now that we’ve defined 3D meat, let’s see what 3D food and 3D meat are made from.
What Is 3D Food Made Of?
3D food can be made using any ingredient as long as it adheres to the printing technique used. Some of these techniques include:
- Extrusion-based printing
- Selective laser sintering
- Hot-melt and room-temperature extrusion
- Inkjet printing
- Binder jetting
- Multi-printhead and multi-material printing
Most 3D food involves the following ingredients:
- Puree
- Mashed potatoes
- Jelly
- Cheese
- Frosting
- Chocolate
- Sugar
- Chocolate powder
- Protein powder
- Sauces (ketchup, pizza, hot sauce, mustard, etc.)
- Colored food ink
For 3D-printed meat, this list of ingredients can include plant-based ingredients such as peas, chickpeas, beetroot, etc., or cultured animal cells.
How Is 3D Printed Cultured Meat Made?
Lab-grown cultured 3D meat is produced using bovine stem cells from a cow or chicken egg. Also known as starter cells, these are isolated and grown in a bioreactor to produce a large quantity of biomass. The cells are then differentiated into edible tissue of muscle and fat cells that are printed into the meat we know and enjoy. Consumers can rest assured that this is an entirely harmless procedure.
This process is further broken down into steps that may differ based on the technology and company producing it.
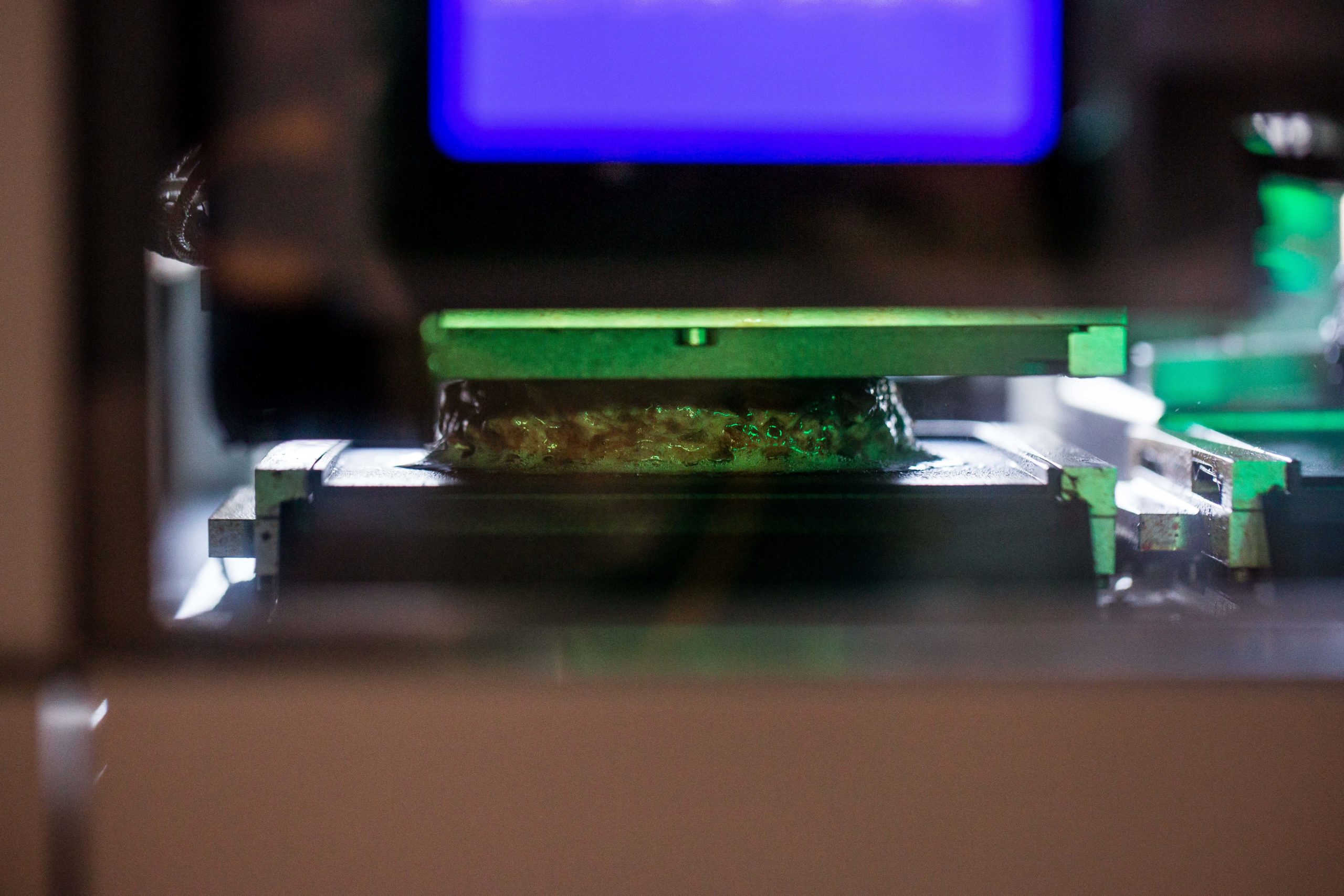
Is 3D-Printed Meat Vegan/Vegetarian?
3D-printed meat may or may not be vegetarian, depending on the ingredients used to ‘print’ it.
Some 3D-printed meat is made using plant-based ingredients such as soy, pea protein, beetroot, chickpeas, and coconut fat. While other varieties of 3D meat — also known as cultured meat — are made using animal cells.
While there is technically no ethical violation in eating printed meat made using cultured animal cells, some vegans and vegetarians might disagree.
At present, there is limited regulatory oversight involved in 3D printing food. But with an increasing number of vegans and vegetarians adapting to the idea of 3D-printed meat or cultured meat, regulation will follow soon.
Is 3D Meat Healthy?
Here are some of the health benefits of 3D meat when compared to consuming livestock-based meats:
- Lower risk of cardiovascular disease
- Lower risk of diabetes
- Lower risk of certain types of cancer
- And more.
Nutritious Content in 3D Meats
The best thing about 3D meat is that it can be found in various nutritional constituencies. Depending on health conditions or dietary requirements, 3D meat can be made to cater to people with celiac disease, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and more.
Since 3D meat is made of plant-based ingredients or cultured cells, its nutritional value is typically much higher than regular meat. These alt-meats provide more nutritious supplements without any harmful content, like unhealthy fats.
3D Meat: The Expenses Involved
At present, 3D printing meat can involve high cost of production, which makes the resulting product prohibitively expensive.
Commercial-grade 3D printers cost thousands of dollars. Every element must be top-grade, from the materials and filaments to the machine itself. And with a relatively small scale of production, this can mean incredibly high production costs overall.
The filaments used in 3D printers also require quite a bit of processing to make them safe for food production. Add to that the time spent learning how to handle these devices properly, and this endeavor becomes even more resource-intensive.
Using cheaper alternatives comes with safety risks and machine troubles—two things that must be avoided.
Is 3D Meat Eco-Friendly?
Yes, 3D meat is eco-friendly.
3D printing uses fewer resources to produce a cultured lab-grown piece of steak than the complex processes needed to make the real thing. More importantly, it doesn’t require raising livestock, slaughtering, or processing meat.
The process of 3D printing also allows for the use of meat by-products to print a steak, thereby reducing the amount of waste that goes out of restaurants.
3D printing also has a lower impact on the environment than other forms of meat processing and production practices.
Currently, the practice of printing meat is one of the best eco-friendly alternatives in the industry. Although, more work is required to make the process affordable for all types of enterprises and customers all over the world. Manufacturers of 3D printers must also find ways to match the production requirements of current food production methods.
In time, these improvements will make the 3D printing process and products an affordable and more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional meat sources.
What Does 3D-Printed Meat Taste Like?
Companies and scientists making 3D-printed meats have claimed that their products taste just like the real thing. But little data backs up this claim since 3D printed meat is not yet accessible for large-scale consumption.
The technology used to create 3D meat aims to recreate the muscle fibers of real meat and its juiciness. This may be as close to getting the taste and texture right.
One recent study attempted to use 3D printing to replicate prized Wagyu beef, with a focus on mimicking the original product’s unique marbling, tenderness, texture, and flavor. While no taste reports are available, getting Wagyu right is sure to be an important milestone in the 3D printed meat industry.
There is also a reluctance to taste lab-grown meat among Gen-Z. This implies the taste of cultured meat is still mainly a matter of perception and will need some getting used to.
Types of Alt-Meat That Can Be Created Using 3D Printing
As 3D meat printing techniques continue to develop, various types of meat can be created. The popular options available to consumers currently include:
- Ground beef
- Burgers
- Lamb
- Kebabs
- Sausages
- And more.
There’s no limit on the type of alternative meats that can be produced using 3D printing.
Reasons to Use 3D Printing to Produce Food
Customization Options
One reason to use 3D printing to produce food is that you can customize the food preparations and alter its taste, flavor, texture, appearance, and more. This helps to ensure better consumer satisfaction, as personalization leads to satisfaction.
Nutritious
3D-printed food is also more nutritious than regular food, thanks to the nutritional control that can be exercised in its production.
From personalized dietary requirements to elderly nutrition, one can control how much protein, sugar, vitamins, minerals, and fats go into 3D-printed food. One can also make softer food products for older adults that fulfill their nutritional requirements.
Sustainability
While plenty of food is being produced to feed everyone in the world, doing so requires a vast amount of natural resources. This has increased the need for sustainable solutions in food production.
One such solution lies in entomophagy, or the consumption of insects. For example, crickets have long been known for their high protein levels. Capturing and processing these insects for consumption requires very few resources, especially compared to other animal protein sources.
While eating crickets as they are might seem strange, 3D printing makes the process more palatable. Using crickets as material for 3D-printed meat will lead to a delicious and nutritious meat alternative. This is one way to explore the sustainable production of food for mass consumption.
When 3D-printed meat becomes more common, it will require little in the way of transportation—an element of food production and distribution that consumes a lot of resources and accounts for tons of greenhouse gas emissions.
Reduction of Food Waste
Leftovers, bruised fruit, meat off-cuts, perishables—there’s no shortage of food waste in every step of the food production and distribution process. Over 1.3 billion tons of food waste is generated every year.
By using 3D printing technology, one can put consumable ingredients to good use and finally solve the global food waste problem.
Reproducibility
With 3D printing technology, consistency is much easier to achieve. These machines are fed recipes that they turn into the ideal product, be it pancakes or burger patties.
Space Exploration
3D food printing is also a great way to provide astronauts with nutritious food alternatives. The customization options are especially useful—these explorers will be able to prepare the meals that they want.
3D-printed food also has a longer shelf life in comparison to freeze-dried food. This means scientists can design space exploration journeys for longer periods without worrying about how long food can last in space.
Why Use 3D Printing to Produce Meat?
3D meat is a smart alternative to traditionally-raised livestock in many ways.
Less Reliance on Livestock
For starters, it’s an obvious solution for those looking to reduce their reliance on livestock. This takes the pressure off the planet by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
With growing climate change concerns, this makes a good case for why you should consider 3D printing to produce meat.
Healthier
3D-printed meat is also much healthier than traditionally sourced meat. You can customize nutrition content, flavor, texture, and other elements to suit the preferences and needs of your consumers.
Vegan and Vegetarian-Friendly
Another huge benefit of producing meat using 3D printing is that it allows manufacturers and restaurants to offer vegan, flexitarian or vegetarian customers delicious meat alternatives.
Better yet, these meat products also live up to the expectations of meat lovers, despite being made with plant-based ingredients.
De-Animalization
Even meat lovers have limits. And some animal parts, while technically edible, are often just thrown away as offcuts.
The solution? De-animalization of meat such as heart, tongue, liver, kidney, intestines, etc.
Typically, these parts would be removed from the meat product. But with 3D printing, they can be used to make more aesthetically pleasing ingredients that taste just as delicious.
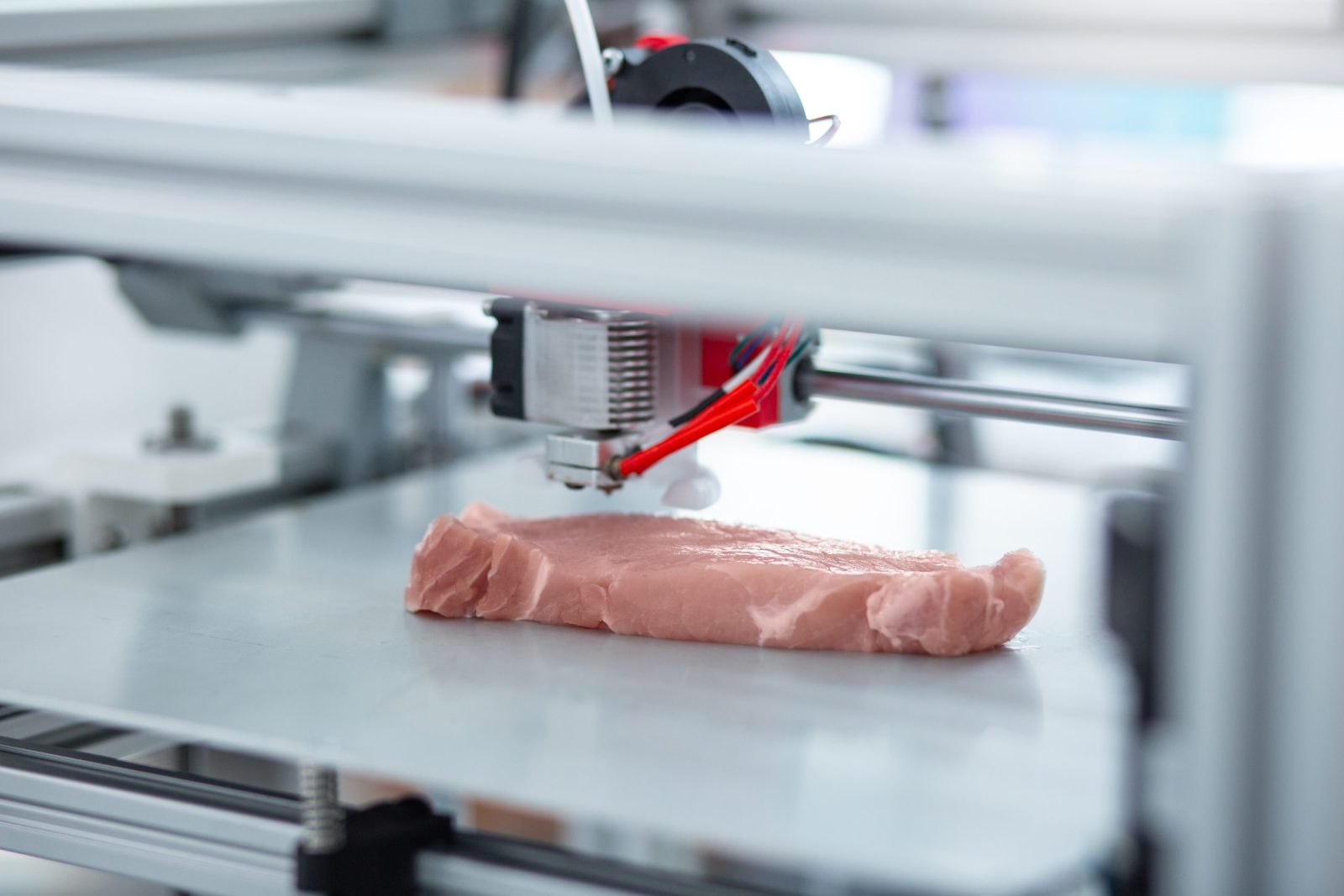

Wrapping Up 3D Meat
Previously just an experimental research field, 3D printing food is now reaching new heights and expanding in popularity. With 3D-printed meat, we’ll soon be resolving the myriad problems caused by the cultivation and slaughter of meat using traditional methods.