With an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.80%, between 2022-2028, robotic technologies are rapidly revolutionizing the global food industry.
Riding on the wave of demand created during the pandemic, many areas of the food industry are now competing to integrate AI and automation tech into their operations.
Here’s a deeper look at the introduction of robotics in the food industry, what the statistics indicate, and the benefits and drawbacks of these lightning-fast advancements.

The Food Industry and the Need for Automation
The food industry is large and complex, encapsulating every process involved in supplying food to the world’s population. This includes production, processing, preservation, packaging, distribution, certification, and other activities.
With the many diverse elements involved in such large-scale operations, most tasks in the food industry are highly intensive in terms of labor and capital.
From rising labor costs and supply chain disruptions to food and workplace safety, the number of problems plaguing the food industry only seems to multiply.
And automation is proving to be the natural solution.
What Is Automation?
Automation is a loaded term with many different applications. In the world of food, it centers around reducing the need for human intervention in monitoring and controlling food production and delivery processes. Automation aims to close the gap created after removing the human element by creating alternative technologies.
These alternate technologies often involve applications such as robotics.
Many, if not all, problems plaguing the food industry today are easily solvable with the use of robotics technology. Given the many advancements in recent years, robotics applications are more adaptable and accessible than ever.
Let’s take a look at real-world examples of robotics in the food industry.
Robotic Technology in the Food Industry
Food service businesses of all types have been quick to adopt robotic technology into their operations. Some popular kinds of robotic technologies being used today include:
- Vision-guided sorting food robotics to sort through produce
- Automated cleaning systems to keep the work environment safe
- Robotic dispensing arm for food decoration and assembly
- Vision systems to read barcodes
- Robotic arms for food handling
- Packaging robots to open, fill, pack, seal, and label packages
- Manufacturing robots
- Computer vision systems to determine the orientation of the manipulated food
- Meal-delivering automated robots
- Robotics to move inventory/boxes
Some of these technologies, like robotic arms, are more versatile than others and hence are used in many different applications.

Are Robots Taking Over the Food Industry?
While food robotics are a fantastic, efficient solution to many problems in the food industry, they’re unlikely to take over all operations anytime soon.
For starters, robotic technology requires human input and management on all levels. And second, there are many food-related tasks that for now, only humans can complete.
Further, robotic technology is only cost-efficient if it optimizes or reduces the operational cost of performing a specific task. Enterprises would and should not spend so much capital on robotics solutions just for the sake of doing so—they should lead to significant returns on their investments.
Looking at the different segments in which food robotics are employed can help explain what areas robots are best deployed.
Applications of Robotic Technology in the Food Industry
Here are a few examples of the various applications of robotics in the food industry:
Food Production, Processing, and Packaging
Food robotics can handle food items with dexterity and package them accurately at a swift pace. With technologies such as vision-guided systems and robotics, it is easier than ever to optimize production, processing, and packaging processes.
Food production and processing typically involve sorting, safety monitoring, picking, cutting, slicing, decorating, etc.
Food packaging involves wrapping food, vacuum sealing, or packing it into containers. It is typically divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging to prepare the food items for distribution and sales.
Here are some examples of the application of food robotics in production, processing, and packaging operations:
Packaging Robots at Atria Scandinavia
Labeling, carton erecting, palletizing, and more—packaging robots are delivering unmatched efficiency in food production.
Automated Meat Processing at Tyson Foods
From deboning to fileting meat, Tyson Foods’ automation solutions aim to substitute machines for its most labor-intensive operations.
Food Service
Robots are working behind the counter too. They are chopping ingredients, flipping burgers, assembling pizzas, mixing cocktails, dispensing condiments, and performing many other tasks much more quickly, efficiently, and accurately than their human counterparts.
These robotics solutions greatly reduce employee health risks while optimizing operations and minimizing waste.
Some popular examples of service robots in the food industry include:
Cafe X’s Coffee-Making Robotic Arm
Cafe X uses a robotic arm to speed up its coffee-making process to serve more customers in a short period. The arm is monitored by a human employee on-site to refill beans and assist customers in ordering.
Miso Robotics’ Flippy
Flippy is an iconic robotic arm that flips burgers, places them on trays, and cleans grill surfaces and equipment.
Robot Mixologist Cecilia.ai
Robotic bartender cecilia.ai can create 120 cocktails per hour with minimum losses and little human contact.
Food Delivery
Food delivery is a high-risk job that saw unprecedented growth in demand due to the pandemic. However, the growth doesn’t translate well to profits due to the cost-intensive nature of the business.
Fortunately, this is an easy avenue for drones and autonomous vehicles to fill in. These vehicles can cater to a small-scale, last mile-style radius much more efficiently. They can also incorporate proper food storage solutions, so all customers get fresh food.
Food robotics can carry more orders and travel longer distances in a single delivery round. They can be operated remotely and come with alarm systems and cameras to deter tampering.
Delivery robots can also work within an indoor establishment. They can navigate shelves and tables. They can bring orders to people in restaurants and deliver room service to hotel guests.
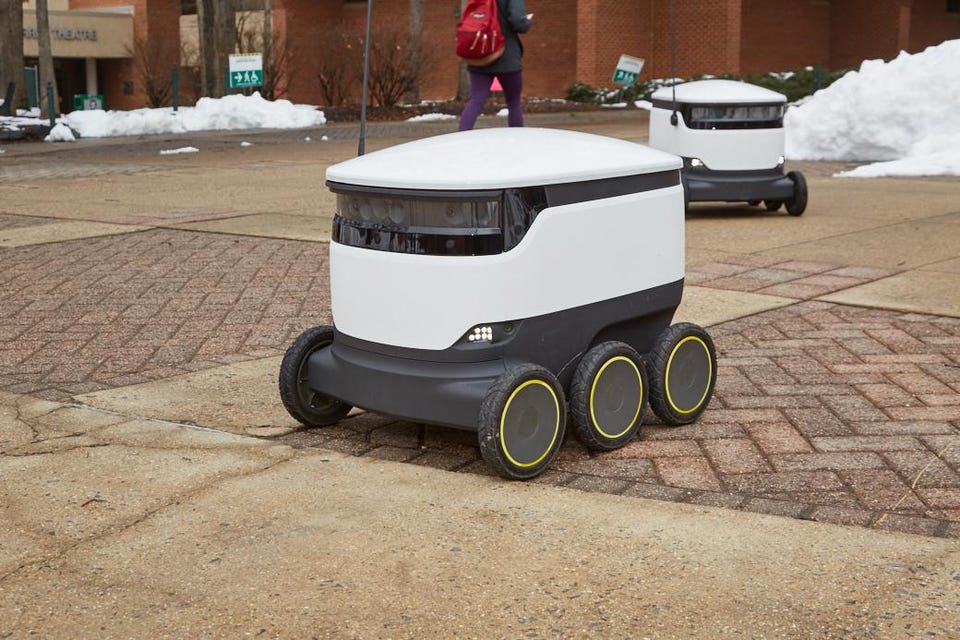

Here are two such examples:
Nuro’s Food Delivering Robots
Uber is testing Nuro’s delivery robots for both short and long trips.
RobotLAB’s ALF Robot
ALF Robot is an indoor autonomous delivery robot that works in restaurants, hotels, hospitals, schools, offices, and other public spaces.
Prevalence of Robotics: Food Processing vs. Food Packaging
Food packaging and food processing involve many operations that are not suitable for humans. Thus, the food packaging sector sees a higher operational gap that robotic technology can easily fill.
Thanks to improved productivity and the high use of packaging, this sector sees the highest CAGR between 2021 and 2028, with food processing following closely.
Infiltration of Robotics into Other Food-Related Fields
The food industry is complex and far-reaching, with robotic technology even more so. Here are some other food-related niches that are seeing an uptick in the application of robotics:
Agriculture
Agriculture lies at the very core of the food industry. Automation in agriculture typically involves the use of robotic tech for the following operations:
- Monitoring and analyzing crop health
- Analyzing soil health
- Getting rid of weeds
- Collecting eggs
- Feeding animals
- Picking mature fruits and vegetables
- Identifying and sorting seedlings
- Planting seeds
- Autonomous milking
- Self-driving tractors for plowing and harvesting crops
- Pesticide application
- Environment analysis to maximize yield
- Autonomous cleaning
- And many more.
From unmanned aerial drones to thermal imaging cameras and robotic arms, many types of robots work in the fields to complete tasks efficiently and safely.
The global market for agriculture robots is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 19.3% between 2021 and 2026. The valuation of the global agriculture robot market is expected to grow from $4.9 billion to $11.9 billion.
Here are some examples of robotics in agriculture:
Merlin Robotic Milker
Merlin is a robotic milking arm. It is the perfect solution to optimize milking operations while ensuring optimum cow health.
Potting Robots from HETO Agrotechnics
A potting robot provides seamless transport of pots to optimize operations and minimize losses due to accidents.
PrecisionHawk’s Drone Mapping and Analytics for Agriculture
PrecisionHawk specializes in aerial intelligence software and products that help companies optimize their operations using geospatial data.
Their agricultural solutions help farmers collect data on acres of crops and analyze farm health so they can make informed decisions that maximize yield.
Grocery Shopping
The introduction of robotic technology in grocery shopping aims to give retailers a competitive advantage in their local market.
Grocery shopping involves all tasks associated with front-of-store customer assistance, cleaning, order fulfillment, delivery, stock-level monitoring, and more.
Using robots to manage inventory could also help you understand and analyze product movement. Then, you can optimize order placement and fulfillment.
Badger Technologies’ Marty
The fully-autonomous robot Marty scans shelves, integrates with your existing stacks, navigates changing environments, and alerts shoppers to in-store hazards.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Robotic Tech in the Food Industry
Benefits
- Reduced Operational Costs
The application of robots in the food industry can help you lower your total operational costs by reducing:
- Floor space
- Production time
- Labor costs
- Resource waste
- And more.
Robots in the food industry also reduce the risk of accidents, thereby reducing losses.
A great example of this is the meat processing industry, wherein food robotics dismantle meat from the bone without the use of knives or other sharp tools. These automated processes result in a superior quality cut of meat and significantly reduce the risks involved in butchery.
- Healthy and Safety Issues
Robots in the food industry reduce employee health risks and food safety risks.
Many tasks in the food industry put employees at risk, such as retrieving hot pizza from an oven or climbing ladders to retrieve ingredients or boxes from storage.
Robots in the food industry also reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses spreading to employees and customers. Automation ensures food products are handled correctly to minimize or even eliminate the risk of large-scale contamination. This was certainly top of mind during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Food robotics solutions are often equipped with specialized (disposable) gloves for hygienic and sanitized processes. Other sanitation efforts involve the use of food-safe materials that can withstand caustic cleaning chemicals or food-safe lubricants for the moving parts of food robotics.
- Meet Supply and Demand
Food robots can work much more quickly and efficiently than humans in all types of operations. Robots in the food industry can also meet supply and demand requirements with little to no adjustment period.
- Increase Employee Satisfaction
Robots in the food industry take over repetitive tasks to leave their human counterparts more time and energy to work on more important things. Humans can find more meaningful work and tackle responsibilities that require intuition, high dexterity, and critical thinking.
- Accuracy
With X-ray and AI technology, food robotics can accurately measure meat parts and portions to deliver superior results. This technology is also helpful for harvesting, sorting, and other tasks that require high accuracy.
- Streamline Your Ordering
Ordering too much food and having to throw them away when they spoil leads to a waste of money. If you order too little and run out of some items in the middle of service, customers will be disappointed when their favorite dish isn’t available anymore. Worse yet, they’ll be disappointed in the restaurant or food service operation for not having enough food, and they will share their experience with others.
To avoid either situation (and thus ensure that customers’ expectations are met), we recommend ordering just enough food for all expected customers during service times. This should leave some extra inventory on hand if unexpected guests show up or if one customer orders an additional side dish or appetizer before leaving their table.
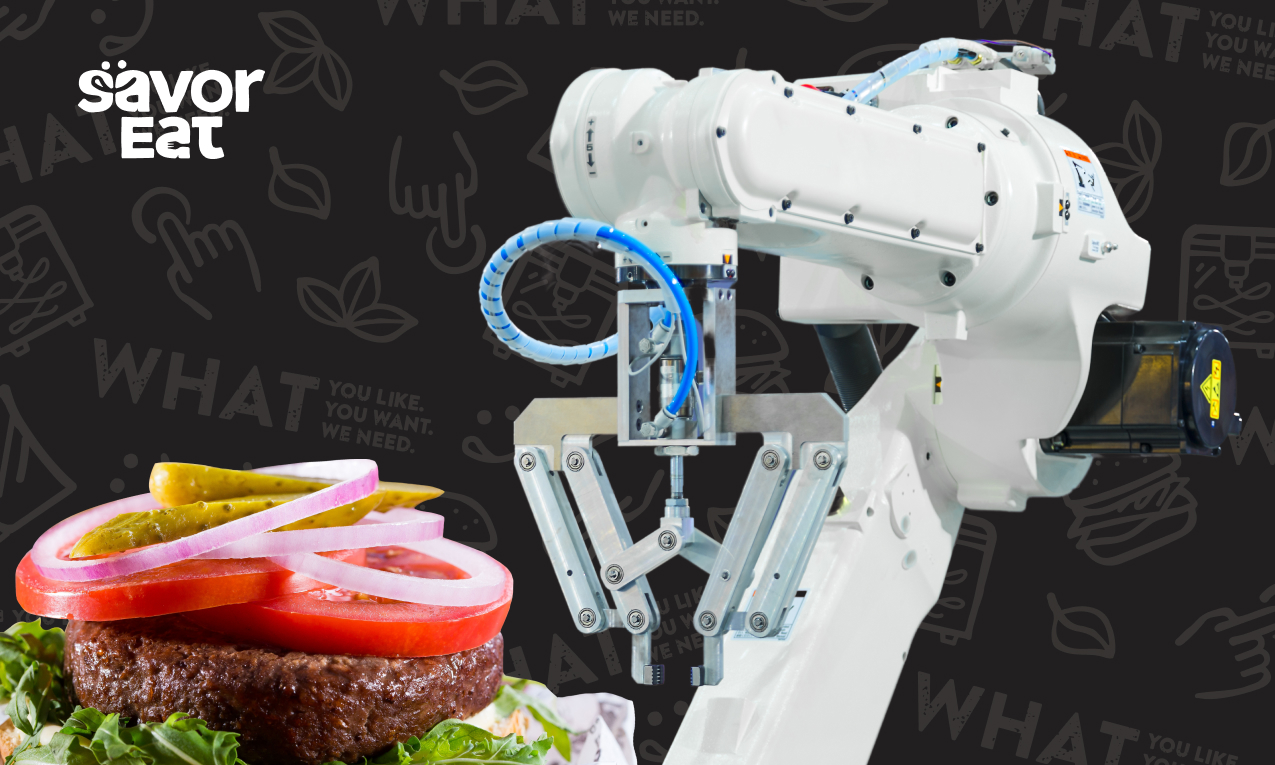
With a robot that produces on-demand meals, such as the SavorEat Smart Robot Chef, you’re significantly lowering the risk of food waste, which continues to be a pervasive issue in the food service industry.
- Track Inventory and Ingredients
One step that can help streamline your food service operations is optimizing your inventory tracking process.
If you do not have an accurate record of the food items in stock at all times, it becomes much more difficult to track how much product needs to be ordered and when they need to come in. This can lead to many problems, such as running out of ingredients unexpectedly or ordering too much product because information was not transferred correctly during a shift change.
Robotics powered by AI or Machine Learning can significantly help with smarter ingredient ordering.
Drawbacks
- High Production Costs
Food robotics are complex instruments, and the machines building them need to be robust, high-performing, and cost-effective. These are the most significant barriers to the large-scale adoption of robotics in the food industry. However, RaaS (Robotics-as-a-Service) is helping to mitigate this barrier to entry for many organizations, making the solution more affordable.
- Training Human Employees to Work With Robots
Despite the large number of autonomous food robotics in the market, the need for human management hasn’t disappeared entirely.
Robots need humans to monitor, operate, and manage them so they can continue performing tasks efficiently. Train staff regularly, but don’t overwhelm them.
Training is an essential part of restaurant operations and food service operations. The more new technology or procedures you introduce into your business, the more training you need to provide to keep everyone on board with these changes.
While it’s important for employees to be trained on newly implemented technologies and procedures, it’s equally important not to overdo it. If employees are constantly bombarded with information overload from too many trainings at once, they may feel overwhelmed and distracted from their main duties.
It’s best to schedule multiple trainings throughout the month rather than all at once. And, if possible, limit each session’s length so that workers can get through everything in a reasonable amount of time without getting overwhelmed by information overload.
Wrapping Up
From higher delivery demands to the increasing global food requirements, there is an urgency to fulfill the food needs of consumers, and quickly. Robotic technology is solving a host of problems that the food industry is facing, as these automated solutions maximize efficiency and minimize waste. Streamlining operations by integrating robotics solutions into your tech stack can help with efficiency and will ultimately improve your food business’s bottom line.